Authentication and Authorization
Overview
DIH has its own security model to manage who can login and what a user can access.
Boot properties
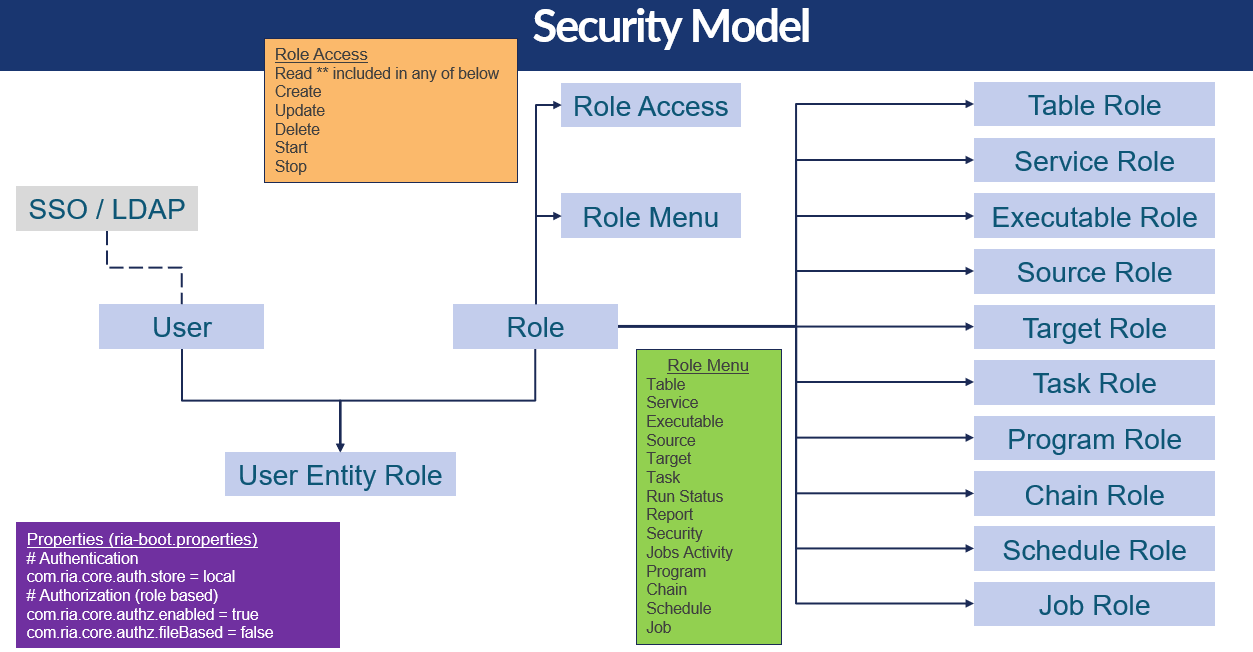
Note that the authorization as described below is only in effect if the ria-boot.properties have been specified as shown in the purple block, bottom-left of the diagram.
User
The UA_AUTH_USER specifies a user id, full name and a password. The password is encrypted and used to authenticate a user at login. If federated SSO or LDAP is used for authentication, the password defined on this table is ignored because the authentication would be done by the SSO provider or LDAP store. The user definition is still required because all the authorization and audit tracking is associated with this user definition.
The User table has an admin user indicator on it which, if set, defines the user as an admin user. An admin user is excluded from all the authorization restrictions described below - it has access to everything.
Role
The UA_AUTH_ROLE specifies a role that restricts what the users linked to the roles may do. The name of the role is user defined. For example, role READ_ONLY could be defined to only grant read access.
A role has one or more role accesses (UA_AUTH_ROLE_ACCESS), which defines the access that the role grants. This can be any combination of read, create, update, delete, start and stop, as shown in the orange block above. All the roles listed below read inherit read access as it won’t make sense for someone to have access to create, update or delete something if they don’t also have read access. In other words, read does not have to be explicitly granted if any of the other roles have been granted.
A role also has to define the Menus (UA_AUTH_ROLE_MENU) that a user assigned to that role may see. The green block above lists the menus that can be specified.
User/Role link
The User Entity Role (UA_AUTH_USER_ENTITY_ROLE) table links users to roles. It provides the many-to-many relationship between the User and Role entities.
Main object roles
Each main object in DIH - Table, Service, Executable, Source, Target, Task, etc. - has a role table (e.g. UA_TASK_ROLE) which specifies the role or roles that that object is a member of. This is the row-level authorization that defines what a user can access, and the type of access (e.g. read, update, etc.).
New object creation and roles
When a user has create privilege, all the roles that are linked to that user are automatically assigned to any new object that the user creates. This is so that newly created objects don’t have to be monitored and linked to roles by an admin user or some external process. All other users with the same access as the user that created the object would automatically and immediately be able to access that object.
Security UI
To manage the authentication and authorization, navigate to Settings > Security.
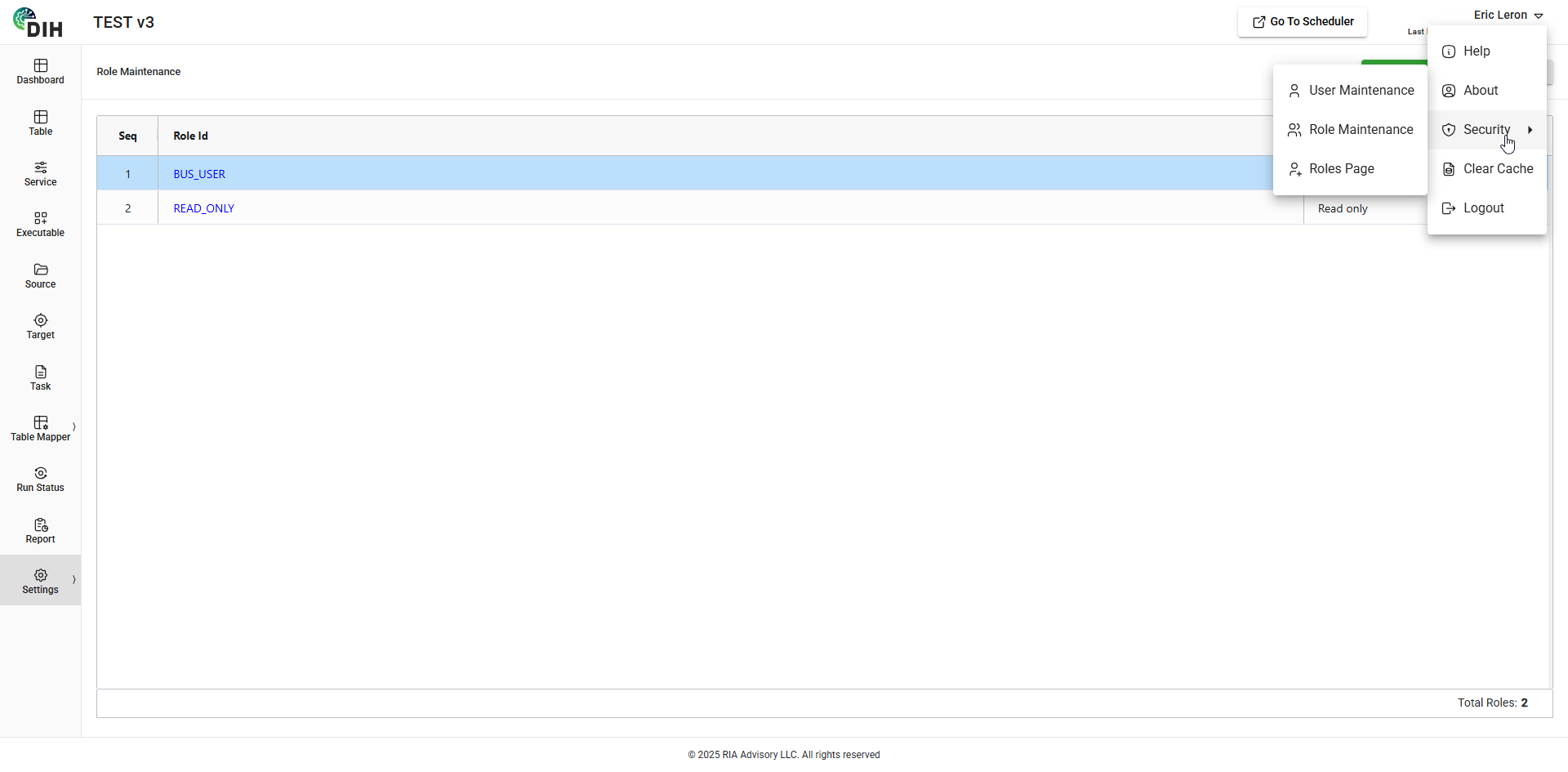
The User Maintenance and Role Maintenance is where the User, Role, Role Access, Role Menu, and User Entity Role entities are maintained.
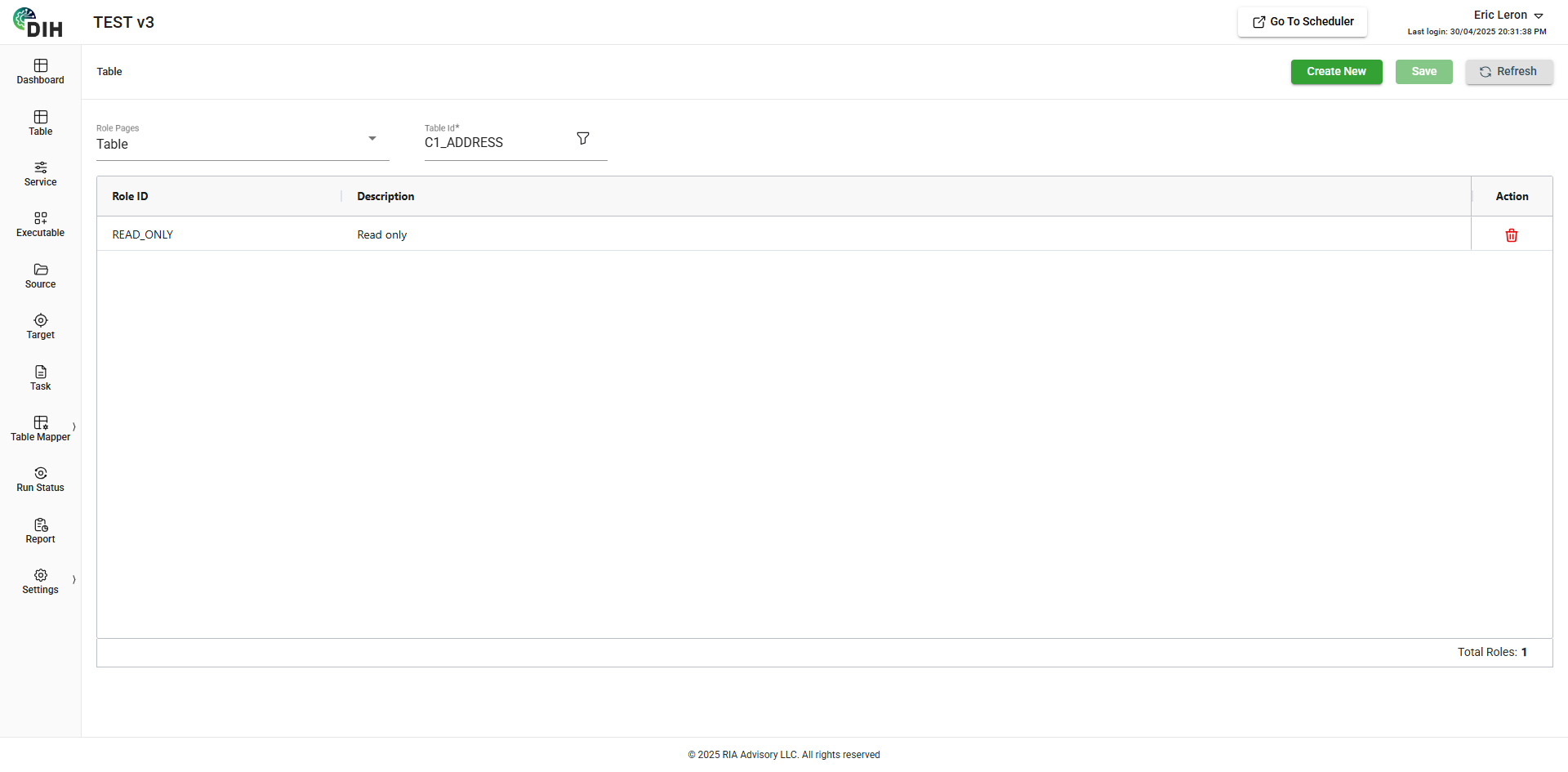
The Roles Page allows you to manage the roles of an entity like Table, Service, Executable, etc. For example, the C1_ADDRESS table has a READ_ONLY role.